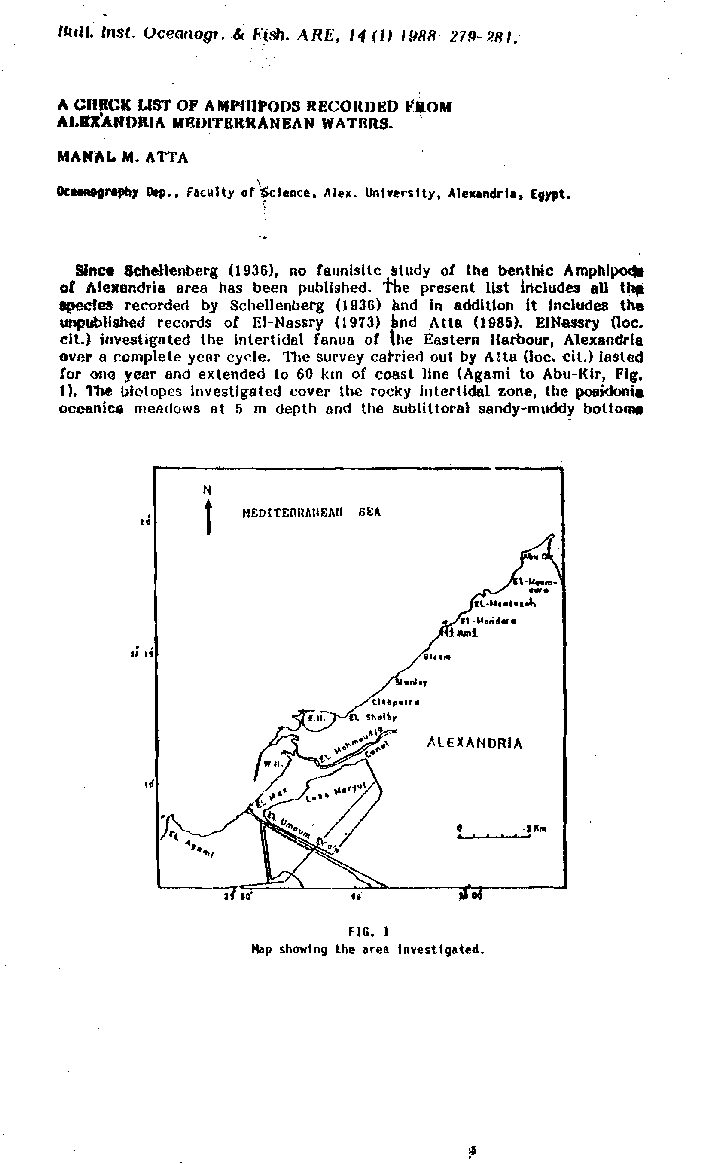
Categories
vol-14CHEMICAL INDICATORS OF WATER POLLUTION IN LAKE MARIUT (EGYPT)
A.A. SAMMAN, M.A. ABDELMONEIM AND F.M. EL-SHARKAWY*
Nattlonal Institute Of Oceanography and Fisheries. Alexandria.
*Hlgh Institute of Public Health. Alexandria University. Alexandria,
ABSTJACT
The polluted basin In lake Harlut (lake
proper) showed certa In cheml ca1 features
associated lfHh sewage and Industrial waste
discharges. The Qalaa Drain water which
15 the main source of water supply to the
basin was also highly polluted. On the
other hand. the fish farm was nearly free
of pollution. The areas subjected to the
direct Influx of sewage effluents and
Industrial wastes were mostly depleted ‘of
dissolved oxygen which tended to Incr~ase
gradually away of pollution. The lake proper’
sustained high val~s of dissolved hydrogen
sulphlde particularly In the polluted areas.
The Inorganic nitrogen compounds were mainly
represented as ammonia. The concentration
of both alllnOnfa and reactive phosphate was
high Indlcatlng Increased load of nutrients.
This reSUlted In a heavy bloom of
phytoplankton particularly blue-green algae.
The average annual values of these components
for the whole basin were 4.41 mg 02/1. 9.0
mg H2S/I. 4.0 mg NIl and 5.26 P04/1.
for the fish far1ll. the average annual
values of both dissolved oxygen and hydrogen·
sulphide were 5.29 mg 0211 and 1.4 mg “2S/l.
The dissolved phosphate and ammonia remained
relatively low and they averaged respectively
0.3 mg P04/1 and 0.8 mg NIL.
The chemical characteristics of the polluted
Qalaa Drain water were reflect.ed In complete
oxygen depletion and high values of dissolved
hydrogen sulphide (average 46.5 mg H2S/1).
The phosphorus and nitrogen loads were also
htgh. reaching an average annual values
of 4.1 mg P04/1 and 6.7 mg NIl.
The water of the Noubarla Canal which
borders the eastern margln of the lake proper
was In general more clear. The dissolved
oxygen In this Canal averaged 5.78 mg 0211
and the hydrogen sulphide was nearly missing.
The dlssolved phosphate and ammonla there
amounted respectivelY to 2.07 mg P04/1 and
1.33 mg NI