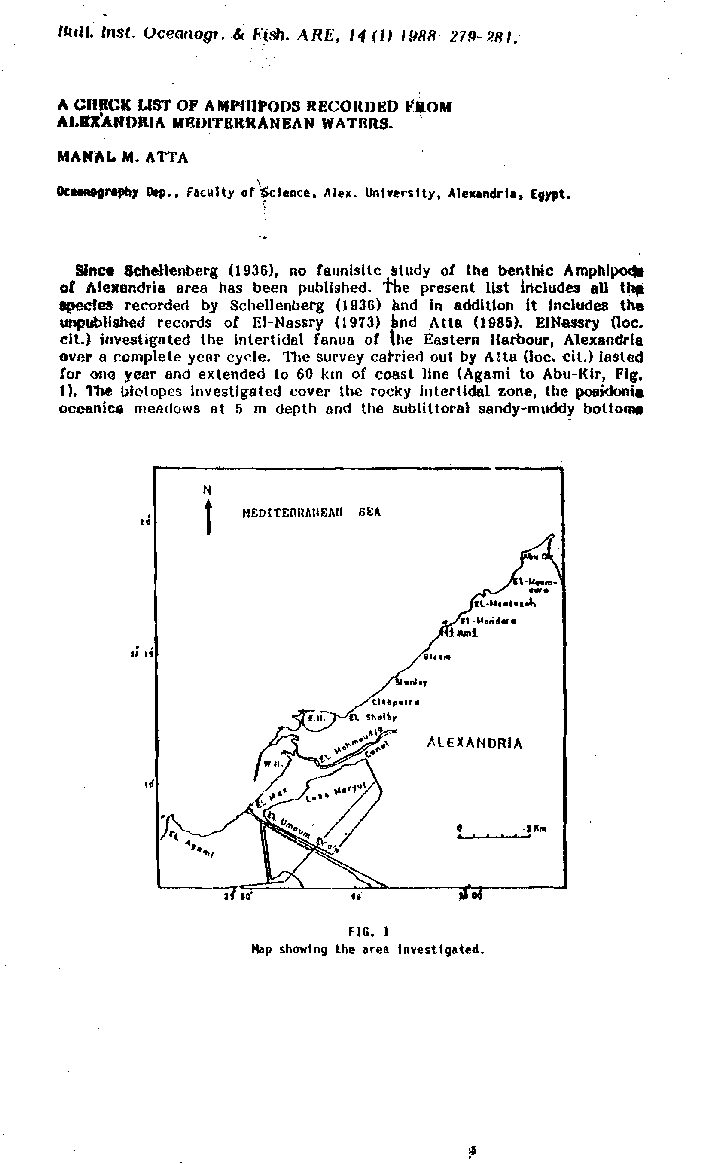
Categories
vol-14PHYTOPLANKTON OF THE EGYPTIAN MEDITERRANEAN WATERS
II-ECOLOGY AND DISTRIBUTION OF THE GENUS CERATIUM SCHRA~l{
N AIM M. DOWIDAR
Department of Oceanography. Faculty of Science. ~lexandria University.
ABSTRACT
The distribution of Ceratia if). the south-eastern
Mediterranean waters along the Egyptian coast was
studied from vertical pla~kton net hauls collected
seasonally dUI’ing 1966. The Ceratilllll population
comprised about 40 species. all of them (except
C. egyptiacta) are indigenous to the eastern
Mediterranean. The population is composed of more
or less tolerant tropi ca1 and coslnOpo litan forms
and is dominated by a limited number of species
viz.: C. contrarium. C. karstenf C. macroceros.
C. massilfense. C. trichoceros. C. carriense. C.
furca, C. fusus and C. extensum.
On the average the population density was lowest
in wint~r and highest in autumn. ‘The region of ElArish harboured the lowest density while that of
the Gulf of Pelusium maintained the lArg~.t
population. In general the population density was
approximately 5 times higher in the inshore neritic
zone tht.1 in the oceanic province. The results were
discussed in relation to the prevailing environmental
conditions.
The genus Cerath.- is one of the important
dinoflagellate genera in the south eastern
Mediterranean water5. Members of this genus constitute
a permanent and sometime common element of the
phytoplankton community in the Egyptian Mediterranean
waters. Some of them descr1 be i nteres t i ng seasonal
and spatial distribution pattern.
Previous studies on this genus in the Mediterranean
waters of Egypt are mostly of qualitative nature
and almost exclussively confined to the inshore
ner1tic waters of Alexandria region (Dowidar and
Allem. 1963 and Halim. 1963). Information on the
occurrence and abundance of these organisms in the
oceanic waters of the south eastern Mediterranean
waters are almost completelY lacking.
The present pa per dea 15 with the ecology.
abundance. .seasonal. and spatial. distribution of
Cerat1U1 species recorded from the south eastern
Mediterranean waters along the Egyptian coast from
rab’s Gulf in the west to El-Arish in the east.
MATEIUAL AND